Wave
A wave can be defined as a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another location.
Wavelength (
Wavelength is the distance covered by one cycle of a wave at given instant. The wavelength should be same for all consecutive cycles and at any two points of a wave its shape repeats. It can also defined as the distance between any two crust or any two trough.
Frequency (f)
Frequency is the number of wave cycles or revolutions per second. a period is the time duration of one cycle.
Frequency (f) = 1/t =1/0.02 =50 HZ.
Relation Between Wavelength( , Frequency(f) and Speed(v)
Speed(v) = wavelength( * Frequency (f).
Audible Frequency
Which range of audio frequency is audible to the average human is called audible frequency. The units of frequency is hertz. The generally accepted standard range of audible frequencies 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. The units of sound is decibels, accepted standard range of audible sound is 0 db to 120 db. Above 120 db sound is harmful to the ears.
Spectrum
Spectrum means classify something in terms of its position on a scale between two extreme points.
Examples of Indian Electromagnetic Spectrum Regulations
1. 0-87.5MHz used for marine and aeronautical navigation
2. 87.5-108MHz used for FM radio broadcast
3. 585-698MHz used for TV broadcast
4. 808-1900MHz used for GSM and CDMA mobile services
5. 2400-2483.5MHz used for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth short range services etc..
2G 3G 4G Spectrum
A wave can be defined as a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another location.
 |
| Waves |
Electromagnetic Waves
During the process of nuclear fusion, sun produces energy that in the form of electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic waves includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma rays. |
| Electromagnetic Waves Travelling from Sun to Earth |
 |
| Electromagnetic Waves |
Different Wavelengths of Electromagnetic Waves
Radio waves have the less energy and frequency and largest wavelength. Gamma rays have the highest energy and frequency and shortest wavelength.
 |
| Electromagnetic Waves with Different Wave Lengths |
Applications of Different Types of Electromagnetic Waves
1. Radio waves - Used to transmit television and radio programmes.
2. Micro wave - Telecommunication and radars.
3. Infrared rays - Used for remotes.
4. Visible light - Used for visible.
5. Ultraviolet rays - Food and drug companies used for sterilize their products.
6. X-Rays - X-Rays are used for purpose.
 |
| Applications of Electromagnetic Waves |
Mobile Communication Through Microwaves
 |
| Mobile Communication through Micro Waves |
Wavelength (
 |
| Wavelength |
Frequency (f)
Frequency is the number of wave cycles or revolutions per second. a period is the time duration of one cycle.
Frequency (f) = 1/t =1/0.02 =50 HZ.
Relation Between Wavelength( , Frequency(f) and Speed(v)
Speed(v) = wavelength( * Frequency (f).
Audible Frequency
Which range of audio frequency is audible to the average human is called audible frequency. The units of frequency is hertz. The generally accepted standard range of audible frequencies 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. The units of sound is decibels, accepted standard range of audible sound is 0 db to 120 db. Above 120 db sound is harmful to the ears.
Spectrum
Spectrum means classify something in terms of its position on a scale between two extreme points.
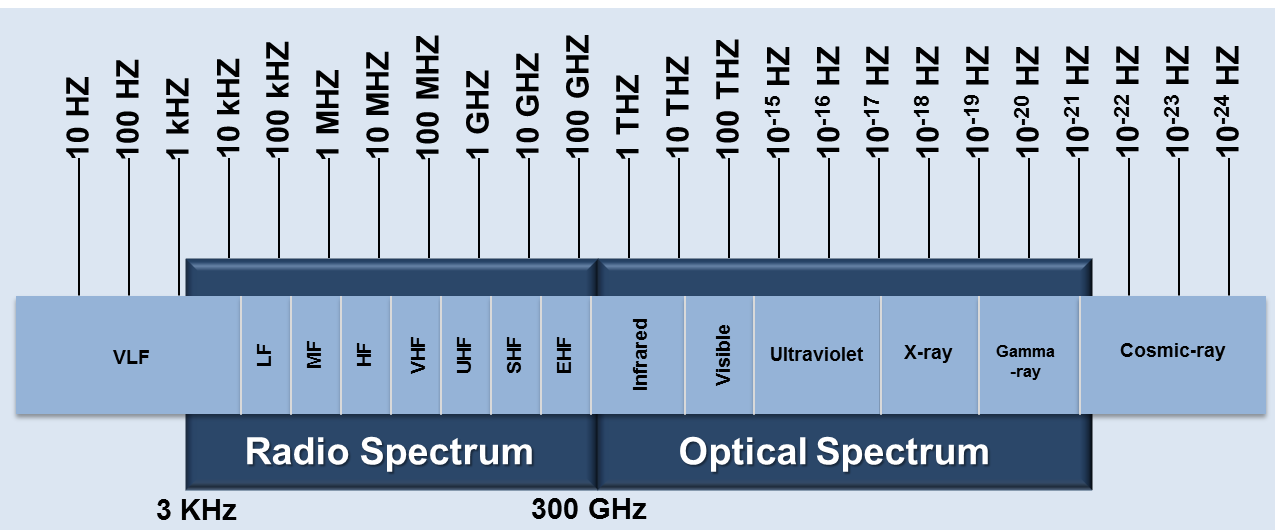 |
| Electromagnetic Spectrum |
Examples of Indian Electromagnetic Spectrum Regulations
1. 0-87.5MHz used for marine and aeronautical navigation
2. 87.5-108MHz used for FM radio broadcast
3. 585-698MHz used for TV broadcast
4. 808-1900MHz used for GSM and CDMA mobile services
5. 2400-2483.5MHz used for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth short range services etc..
2G 3G 4G Spectrum
Wave Theory
 Reviewed by Unknown
on
October 24, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by Unknown
on
October 24, 2017
Rating:
 Reviewed by Unknown
on
October 24, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by Unknown
on
October 24, 2017
Rating:

